Page 56 - FoodFocusThailand No.230 May 2025
P. 56
STRATEGIC R&D
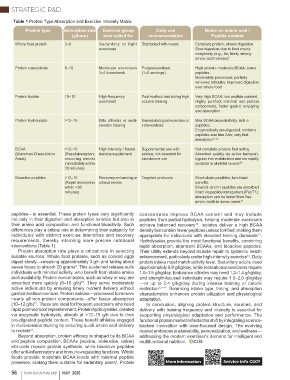
Table 1 Protein Type Absorption and Exercise Intensity Matrix
Protein type Absorption rate Exercise group Daily use Notes on amino acid /
(g/hour) best suited for recommendation Peptide content
Whole food protein 3–6 Sedentary to light Distributed with meals Complete protein; slower digestion.
exercisers Slow digestion due to food matrix
complexity (e.g., fat, fiber); steady
amino acid release) 9
Protein concentrate 8–10 Moderate exercisers Pre/post-workout High protein; moderate BCAA; some
3–4 times/week (1–2 servings) peptides.
Moderately processed; partially
removes fat/carbs; improved digestion
over whole food
Protein isolate 10–12 High-frequency Post-workout and during high Very high BCAA; low peptide content.
exercisers volume training Highly purified; minimal non-protein
components; faster gastric emptying
and absorption
Protein hydrolysate >12–15 Elite athletes or multi- Immediately post-exercise or Max BCAA bioavailability; rich in
session training intra-workout peptides.
Enzymatically pre-digested; contains
peptides and free AAs; very fast
absorption 11,12
BCAA >12–15 High intensity / fasted Supplemental use with Not complete protein; fast acting.
(Branched-Chain Amino (Rapid absorption, training supplement protein, not intended for Absorbed quickly via active transport;
Acids) occurring almost standalone use bypass liver metabolism and are rapidly
immediately within oxidized in skeletal muscle 10
30 minutes)
Bioactive peptides >12–15 Recovery-enhancing or Targeted protocols Short-chain peptides; functional
(Rapid absorption clinical needs benefits.
within <30 Small di- and tri-peptides are absorbed
minutes) intact via peptide transporters (PepT1);
absorption can be faster than free
amino acids in some cases 12
peptides—is essential. These protein types vary significantly concentrates improve BCAA content and may include
not only in their digestion and absorption kinetics but also in peptides from partial hydrolysis, helping moderate exercisers
their amino acid composition and functional bioactivity. Such achieve balanced recovery . Isolates deliver a high BCAA
10
differences play a critical role in determining their suitability for density but contain fewer peptides unless fortified, making them
individuals with distinct exercise intensities and recovery appropriate for individuals with elevated training demands .
11
requirements, thereby informing more precise nutritional Hydrolysates provide the most functional benefits, combining
interventions (Table 1). rapid absorption, abundant BCAAs, and bioactive peptides.
Protein absorption rate plays a critical role in selecting Their utility extends beyond muscle repair to systemic health
suitable sources. Whole food proteins, such as cooked eggs enhancement, particularly under high-intensity exercise . Daily
12
digest slowly—releasing approximately 3 g/h and taking about protein intake must match activity level. Sedentary adults need
9
seven hours to absorb 20 grams . This sustained release suits approximately 0.8 g/kg/day, while recreational exercisers require
individuals with minimal activity, who benefit from stable amino 1.0–1.5 g/kg/day. Endurance athletes may need 1.2–1.4 g/kg/day,
acid availability. Protein concentrates, such as whey or soy, are and strength-focused individuals may require 1.6–2.0 g/kg/day
10
absorbed more quickly (8–10 g/h) . They serve moderately —or up to 2.4 g/kg/day during intense training or caloric
active individuals by ensuring timely nutrient delivery without restriction 12–14 . Balancing intake type, timing, and absorption
gastrointestinal overload. Protein isolates—processed to remove characteristics enhances protein utilization and physiological
nearly all non-protein components—offer faster absorption adaptation.
11
(10–12 g/h) . These are ideal for frequent exercisers who need In conclusion, aligning protein structure, sources, and
rapid post-workout replenishment. Protein hydrolysates, created delivery with training frequency and intensity is essential for
via enzymatic hydrolysis, absorb at >12–15 g/h due to their supporting physiological adaptation and performance. The
pre-digested peptide content. These benefit athletes engaged functional protein market reflects this shift by integrating science-
in multi-session training by ensuring quick amino acid delivery backed innovation with user-focused design. The evolving
to muscle . market embraces sustainability, personalization, and wellness—
11
Beyond absorption, protein efficacy is shaped by its BCAA addressing the modern exerciser’s demand for intelligent and
and peptide composition. BCAAs (leucine, isoleucine, valine) multifunctional nutrition.
stimulate muscle protein synthesis, while bioactive peptides
offer anti-inflammatory and immune-regulating functions. Whole
foods provide moderate BCAA levels with minimal peptide
9
presence, making them suitable for sedentary users . Protein More Information Service Info C007
56 FOOD FOCUS THAILAND MAY 2025
24/4/2568 BE 13:37
52-56_Strategic R&D_����.indd 56 24/4/2568 BE 13:37
52-56_Strategic R&D_����.indd 56