Page 72 - FoodFocusThailand No.232 July 2025
P. 72
two main types of mass transfer: (1) water moves
out of the food into the osmotic solution, and (2)
some components of the osmotic solution (sugars
or salts) diffuse into the food matrix. Moreover,
these soluble compounds, including minerals,
organic acids, and vitamins, can affect the sensory
qualities and nutritional content of the final
product. After osmotic treatment, the food
undergoes freezing, which lowers its temperature
below the freezing point and converts the
remaining water into ice. The performance of this
process depends on several factors, including the
type of product, the composition of the osmotic
solution, and the process conditions. A higher
osmotic mass transfer rate is typically favorable,
as it helps reduce the loss of essential nutrients.
This rate is influenced by the food sample’s
dimensions, which increase its surface area and
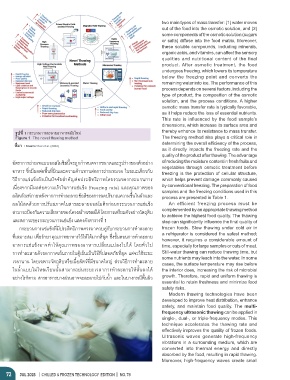
รููปที่่� 1 กระบวนี้การละลายอัาหารสมัยใหม่ thereby enhance its resistance to mass transfer.
Figure 1 The novel thawing method The freezing method also plays a critical role in
determining the overall efficiency of the process,
ที่่�มา / Source: Koc et al. (2022)
as it directly impacts the freezing rate and the
quality of the product after thawing. The advantage
อััตราการถ่่ายเทแบบอัอัสโมซิิสนี้้�จะถู่กกำาหนี้ดจากขนี้าดและรูปร่างขอังตัวอัย่าง of reducing the moisture content in fresh fruits and
อัาหาร ซิ่�งม้ผลต่อัพื้้�นี้ท้�ผิวและความต้านี้ทานี้ต่อัการถ่่ายเทมวล ในี้ขณะเด้ยวกันี้ vegetables through osmotic treatment before
freezing is the protection of cellular structure,
วิธี้การแช่่แข็งยังเป็นี้ปัจจัยสำาคัญต่อัประสิทธีิภาพื้โดยรวมขอังกระบวนี้การ which helps prevent damage commonly caused
เนี้้�อังจากม้ผลต่อัความเร็วในี้การแช่่แข็ง (freezing rate) และคุณภาพื้ขอัง by conventional freezing. The preparation of food
ผลิตภัณฑ์์ภายหลังจากการทำาละลาย ข้อัด้ขอังการลดปริมาณความช่้�นี้ในี้ผักและ samples and the freezing conditions used in this
process are presented in Table 1.
ผลไม้สดด้วยการปรับสภาพื้ในี้สารละลายอัอัสโมติกก่อันี้กระบวนี้การแช่่แข็ง An efficient freezing process must be
สามารถ่ป้อังกันี้ความเส้ยหายขอังโครงสร้างเซิลล์ได้ โดยการเตร้ยมตัวอัย่างวัตถุ่ดิบ complemented by an appropriate thawing method
และสภาวะขอังกระบวนี้การแช่่แข็ง แสดงดังตารางท้� 1 to achieve the highest food quality. The thawing
step can significantly influence the final quality of
กระบวนี้การแช่่แข็งท้�ม้ประสิทธีิภาพื้ควรมาควบคู่กับกระบวนี้การทำาละลาย frozen foods. Slow thawing under cold air in
ท้�เหมาะสม เพื้้�อัรักษาคุณภาพื้อัาหารไว้ให้ได้มากท้�สุด ซิ่�งขั�นี้ตอันี้การทำาละลาย a refrigerator is considered the safest method;
however, it requires a considerable amount of
อัาหารแช่่แข็งอัาจทำาให้คุณภาพื้ขอังอัาหารเปล้�ยนี้แปลงไปได้ โดยทั�วไป time, especially for large samples or cuts of meat.
การทำาละลายด้วยอัากาศเย็นี้ภายในี้ตู้เย็นี้เป็นี้วิธี้ท้�ปลอัดภัยท้�สุด แต่จะใช่้ระยะ Still-water thawing can reduce thawing time, but
เวลานี้านี้ โดยเฉพื้าะวัตถุ่ดิบหร้อัเนี้้�อัสัตว์ท้�ม้ขนี้าดใหญ่ ส่วนี้วิธี้การทำาละลาย some nutrients may leach into the water. In some
cases, the surface temperature may rise before
ในี้นี้ำ�าแบบไม่ไหลเว้ยนี้นี้ั�นี้สามารถ่ย่นี้ระยะเวลาการทำาละลายให้สั�นี้ลงได้ the interior does, increasing the risk of microbial
อัย่างไรก็ตาม สารอัาหารบางส่วนี้อัาจจะละลายไปกับนี้ำ�า และในี้บางกรณ้พื้้�นี้ผิว growth. Therefore, rapid and uniform thawing is
essential to retain freshness and minimize food
safety risks.
Modern thawing technologies have been
developed to improve heat distribution, enhance
safety, and maintain food quality. The multi-
frequency ultrasonic thawing can be applied in
single-, dual-, or triple-frequency modes. This
technique accelerates the thawing rate and
effectively improves the quality of frozen foods.
Ultrasonic waves generate high-frequency
vibrations in a surrounding medium, which are
converted into thermal energy and directly
absorbed by the food, resulting in rapid thawing.
Moreover, high-frequency waves create small
72 JUL 2025 CHILLED & FROZEN TECHNOLOGY EDITION NO. 78
24/6/2568 BE 16:38
68-73_��������� 4.indd 72
68-73_��������� 4.indd 72 24/6/2568 BE 16:38